On-Farm Antimicrobial Usage in Broiler Chicken Production
On-Farm Antimicrobial Usage in Broiler Chicken Production
New Antibiotic Data Dashboard
We are proud to release a new interactive dashboard of on-farm antimicrobial use data for broiler chickens and turkeys.
Broiler companies participated voluntarily and represented a large percentage of the overall U.S. broiler chicken production
- The antimicrobial use datasets represent approximately 85% of broiler chickens produced annually, based on USDA:National Agricultural Statistics Service published numbers
- The antimicrobial use data that were submitted for 2022 include information on approximately 8,460,000,000 chicks placed, 7,990,000,000 chickens slaughtered, and 51,680,000,000 pounds liveweight produced
2023
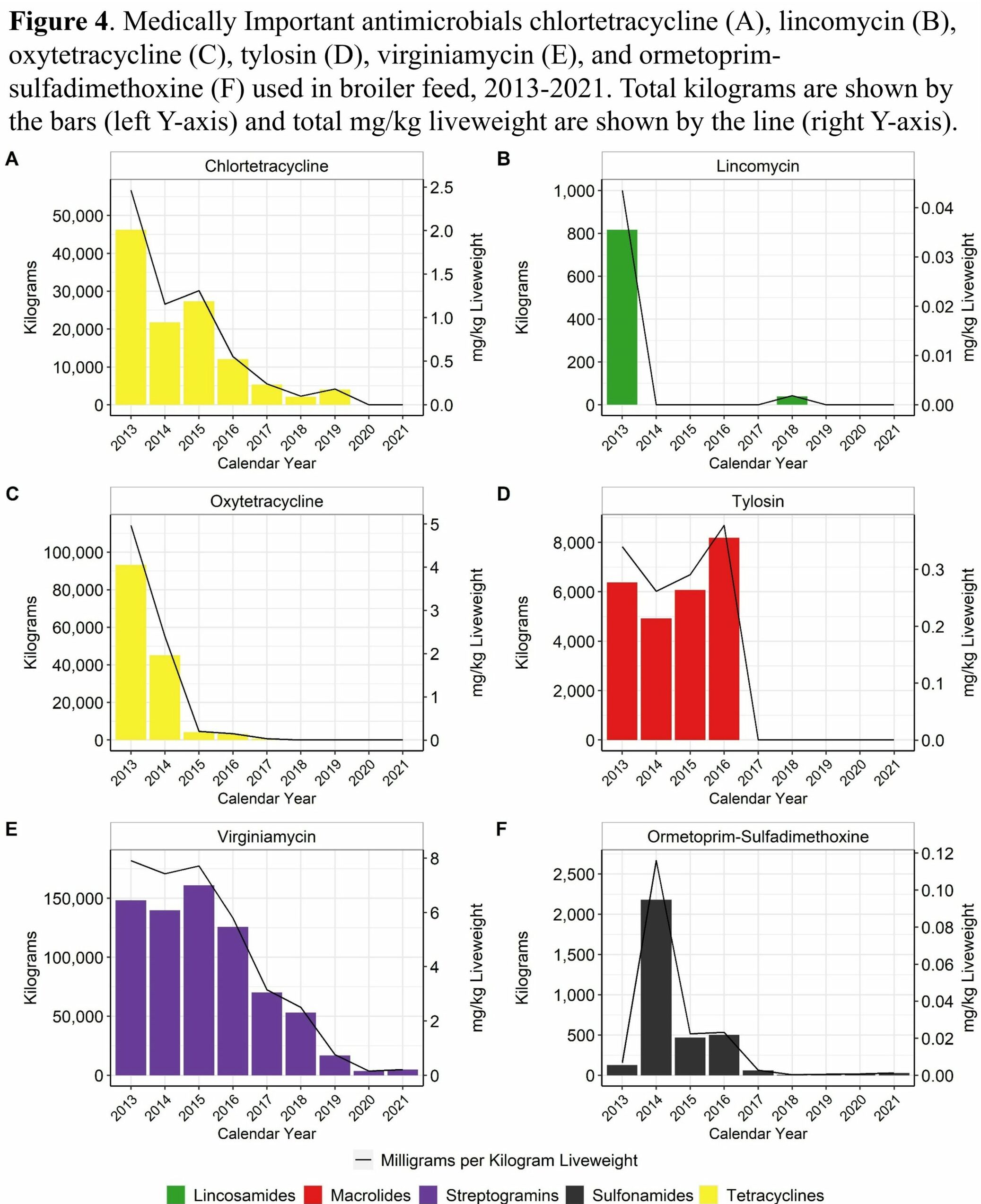
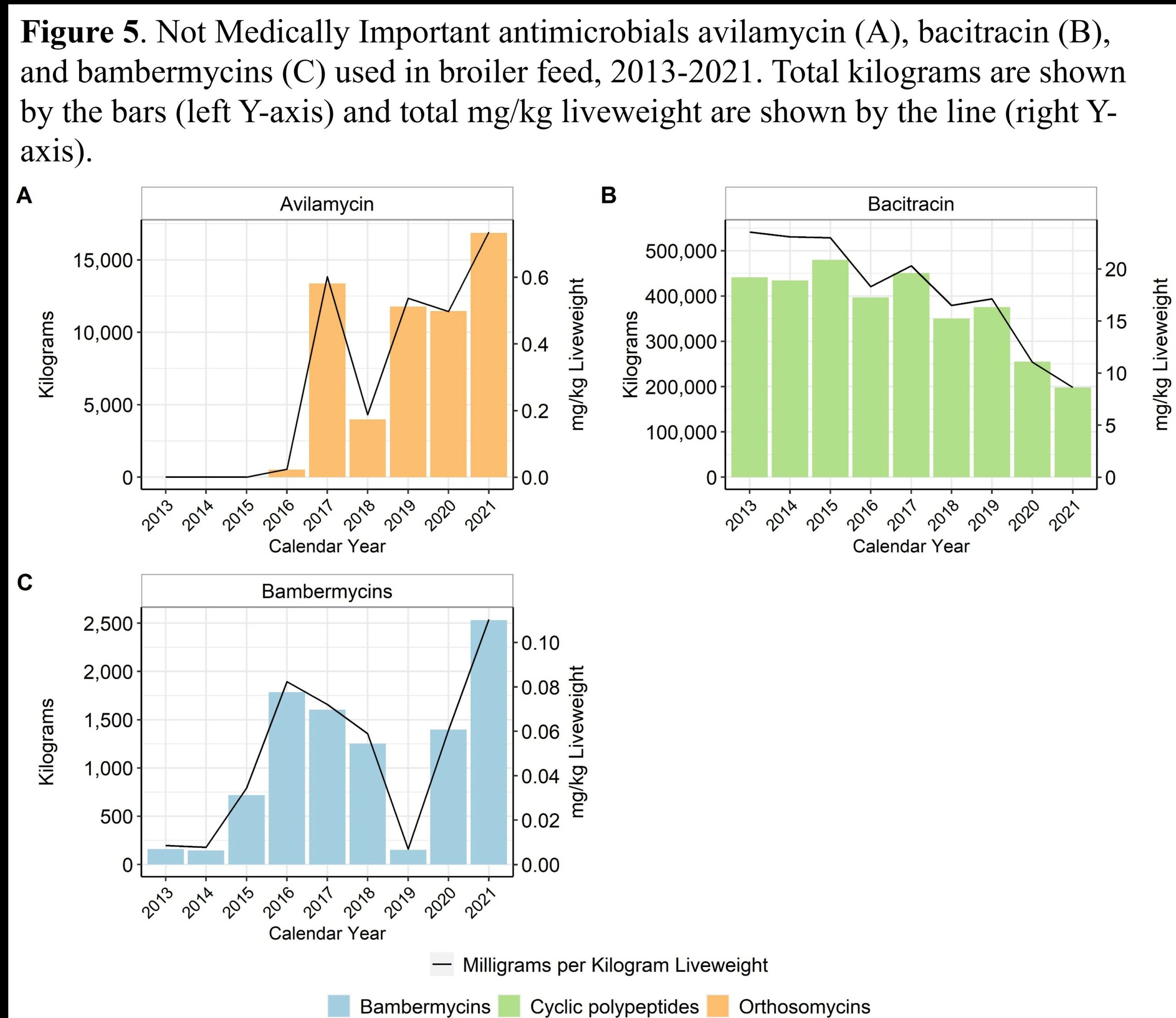
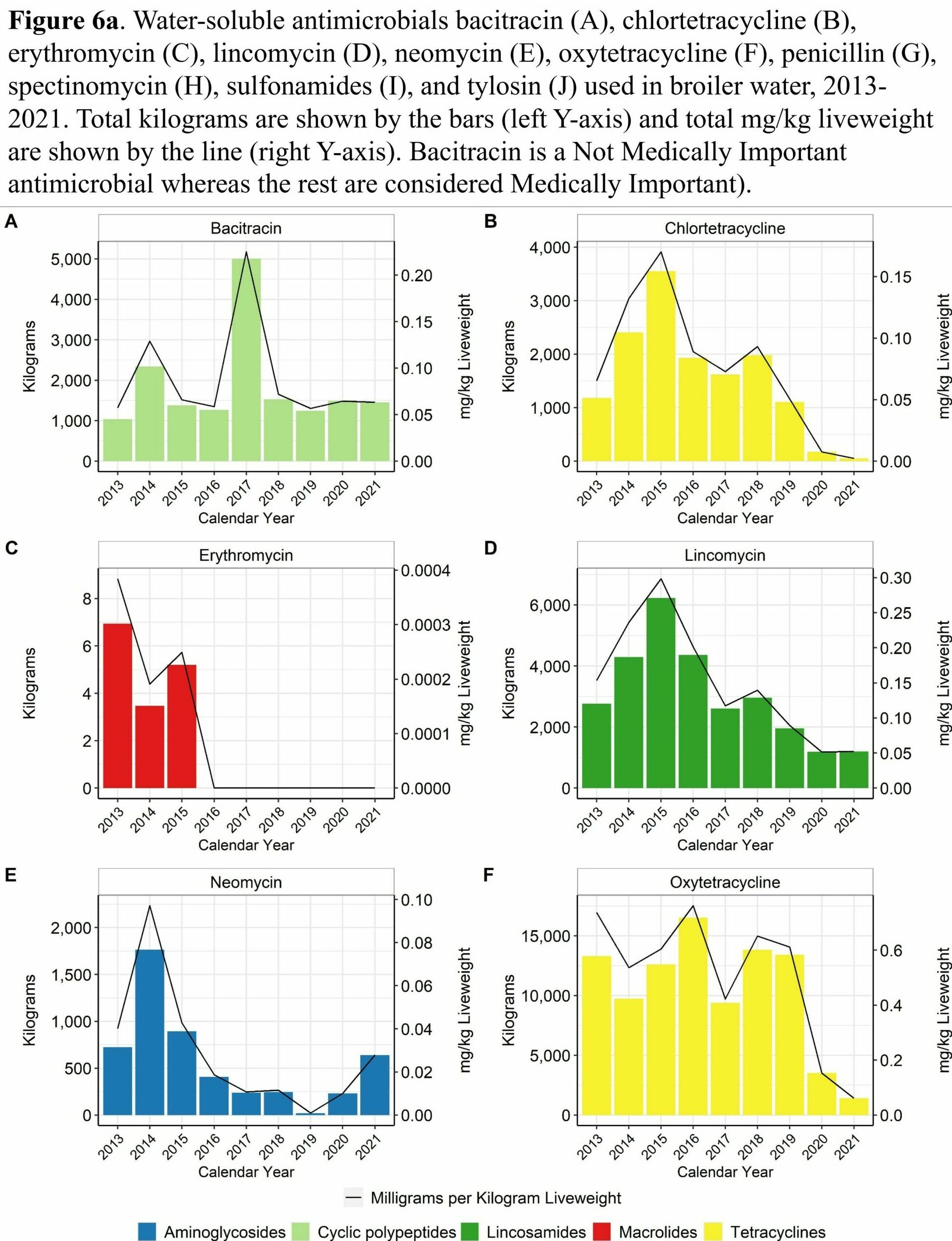
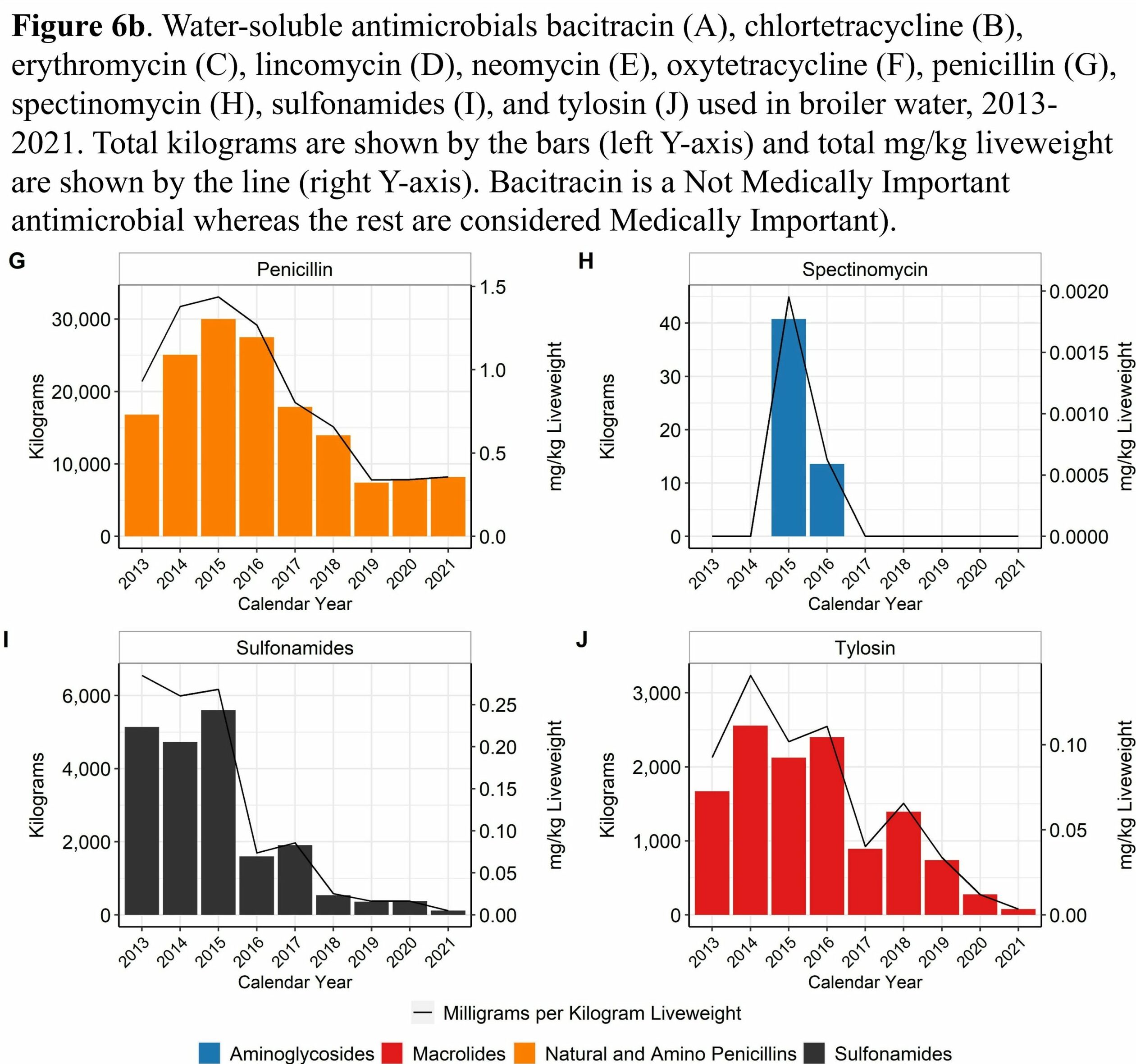
Antimicrobial usage in broiler chicken production in the United States, 2013–2021
Randall S. Singer, Nora F. D. Schrag, Isabel Ricke, Michael D. Apley
Frontiers in veterinary science. 2023; vol. 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2023.11399082020
Randall S. Singer, Leah J. Porter, Nora F. D. Schrag, Peter R. Davies, Michael D. Apley, Kathe Bjork
Zoonoses Public Health. 2020; 67(Suppl. 1): 22– 35. https://doi.org/10.1111/zph.12764
Key Findings
Several key diseases were targeted by antimicrobial administration
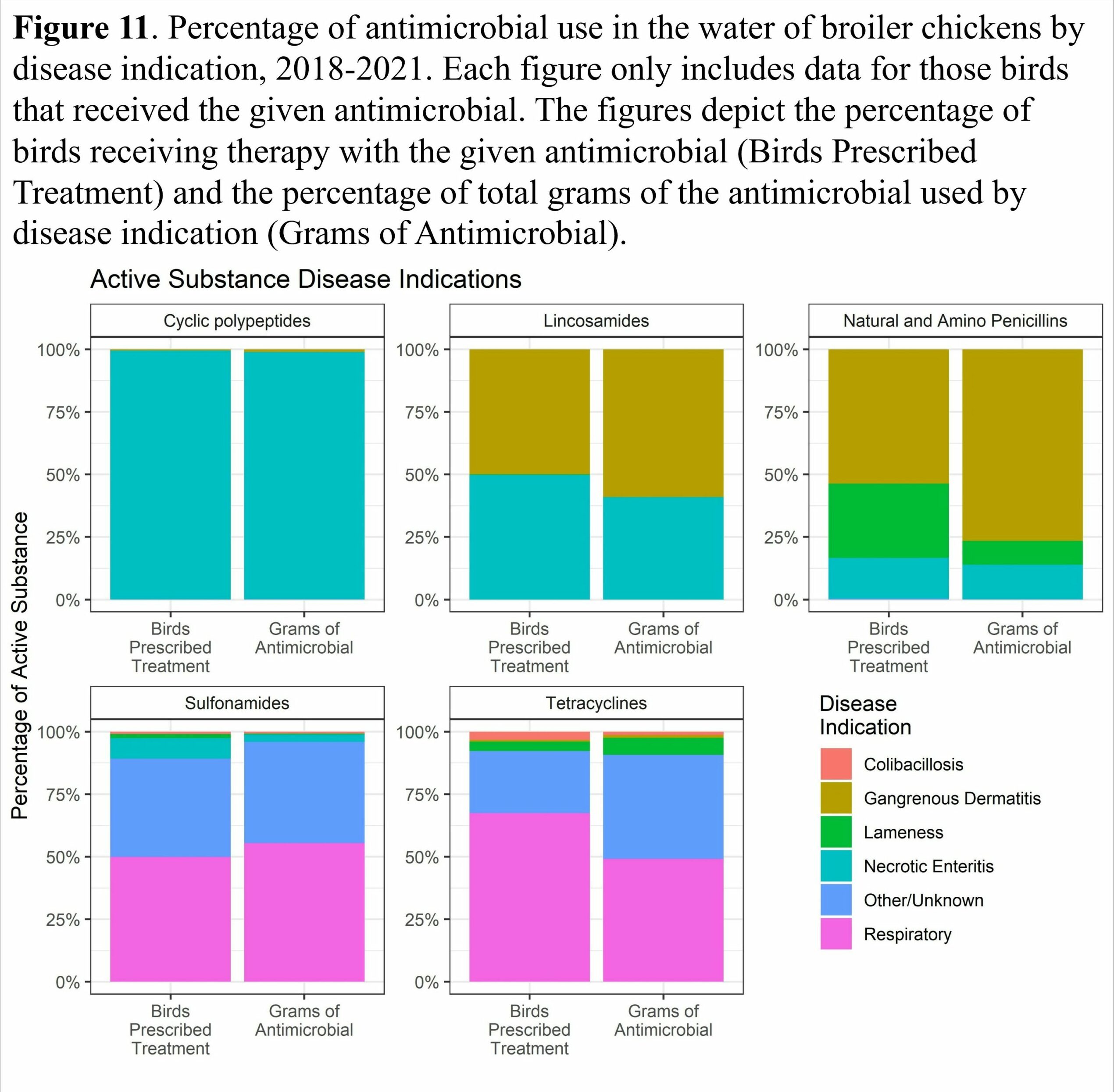
- Necrotic enteritis, a clostridial disease of chickens, remains one of the most important diseases of chickens that requires antimicrobial therapy
- Colibacillosis, a broad category of E. coli diseases that affect chickens, results in much of the antimicrobial use in feed and water. Many of the respiratory diseases affecting chickens are caused by E. coli
- Clostridial dermatitis, another clostridial disease, necessitates a considerable fraction of the overall antimicrobial use in chicken production
Antimicrobial use by all routes decreased substantially between 2013 and 2022
Hatchery Antimicrobials
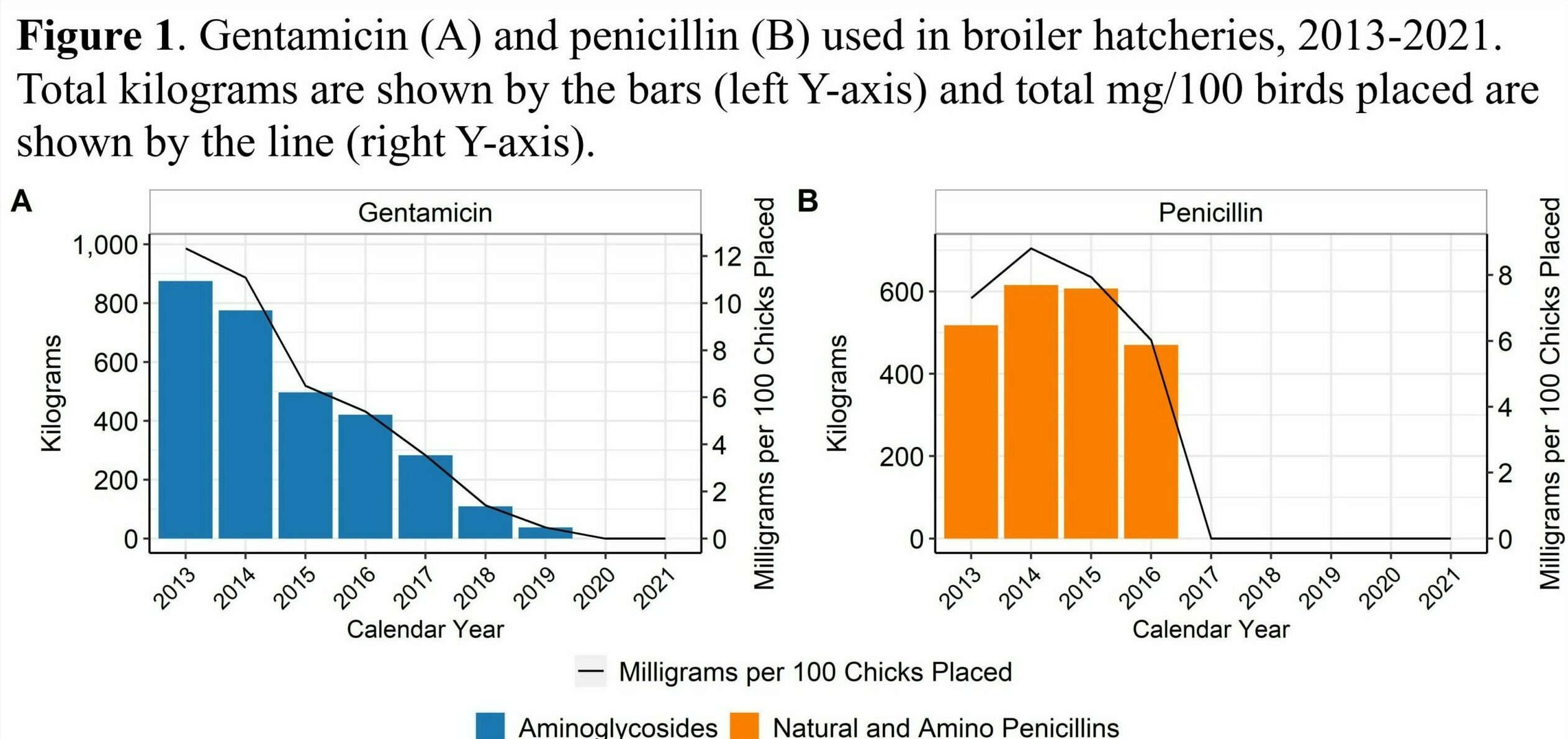
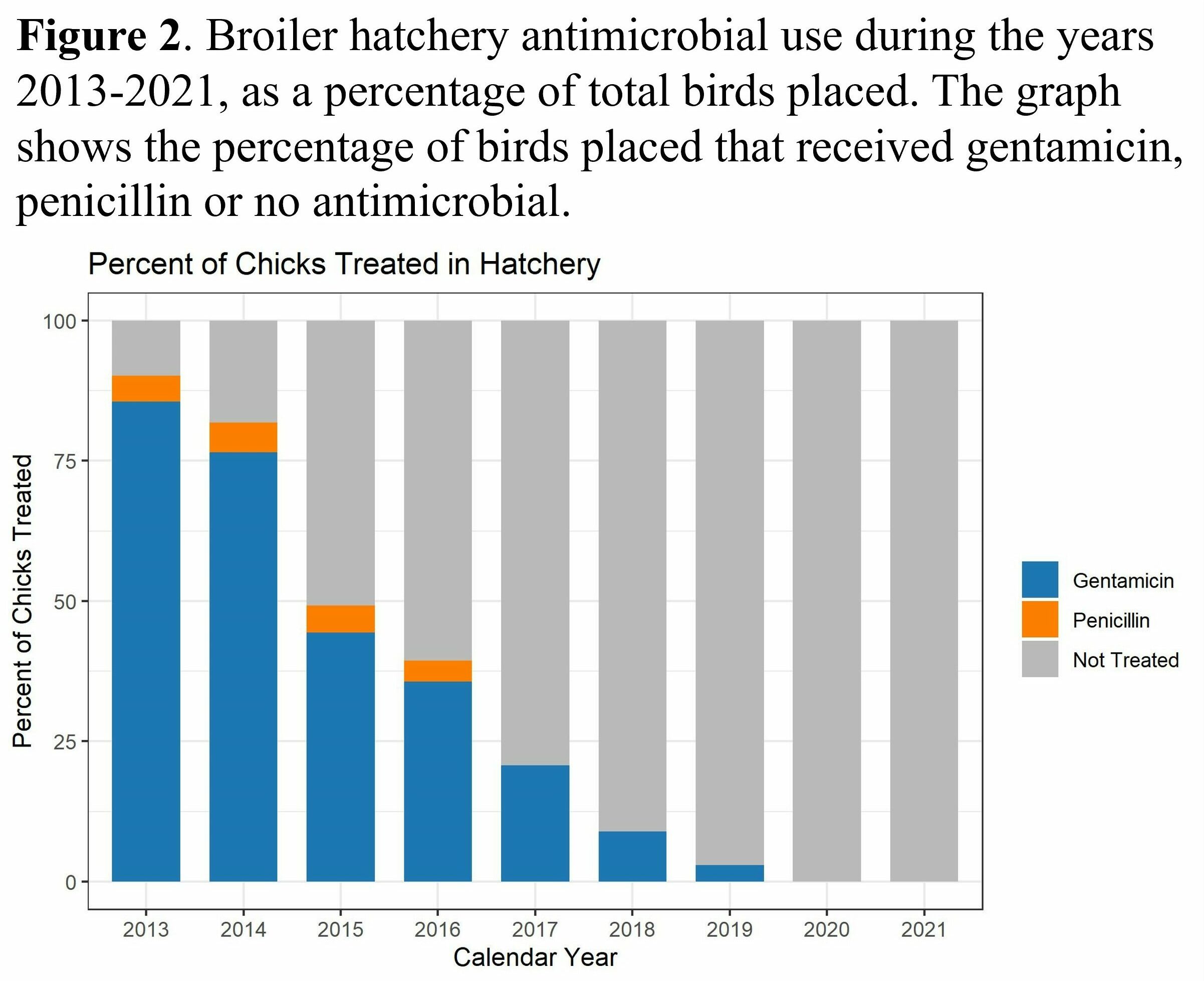
- The approximate percentage of broiler chicks placed that received hatchery antimicrobials decreased from 90% in 2013 to less than 1% in 2022
- Hatchery gentamicin use in broiler chicks decreased approximately 71% between 2013 and 2017 and has remained minimal through 2022
In-Feed Antimicrobials
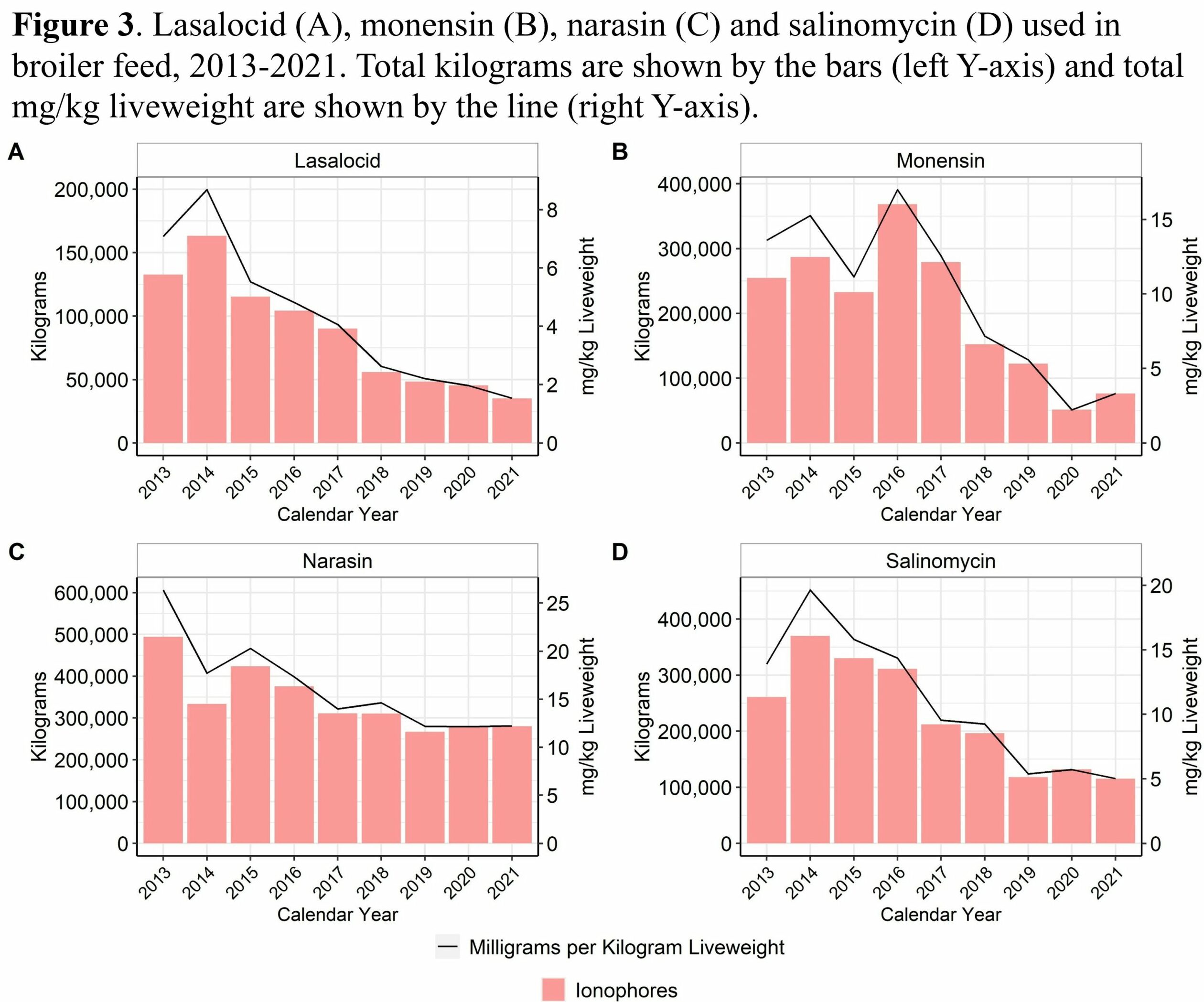
- In-feed virginiamycin use decreased approximately 97% between 2013 and 2022
- In-feed tetracycline use decreased approximately 96% between 2013 and 2017 and has not been used since 2020
Water-Soluble Antimicrobials
- Medically important water-soluble antibiotic use in broiler chickens decreased substantially 2013-2020 but has increased for some antibiotics from 2020-2022
- Water-soluble penicillin use decreased 64% from 2013-2019 but has increased 22% from 2019-2022 due to increases in gangrenous (clostridial) dermatitis incidence
- Water-soluble tetracycline use decreased by more than 87% since 2013
- Water-soluble lincomycin use decreased 66% from 2013-2020 but has increased 28% from 2020-2022 due to increases in gangrenous (clostridial) dermatitis incidence
- Water-soluble sulfonamide use decreased by 96% since 2013
- Medically important water-soluble antibiotic use in broiler chickens decreased substantially 2013-2020 but has increased for some antibiotics from 2020-2022
There was a shift to greater use of antimicrobial drugs that are not medically-important
- In-feed and water-soluble bacitracin remained a commonly-used antimicrobial drug for the prevention and treatment of necrotic enteritis
- In-feed avilamycin use increased, as it is a not medically important antimicrobial drug for the prevention of necrotic enteritis
There were substantial reductions in the use of most medically important antimicrobials in broiler production, regardless of route of administration
- While a reduction in antimicrobial use may be an important indicator of improved stewardship, reducing the need for antimicrobials through improved disease prevention should be considered a more holistic indicator of overall flock health and optimal antimicrobial use
Acknowledgments
This project is funded with multiple annual grants from the U.S. Poultry & Egg Association. The project was also partly supported from 2016 to 2023 under a cooperative agreement with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (U01FD005878). This ongoing monitoring program would not be possible without the voluntary participation of layer, broiler chicken and turkey companies of the U.S. as well as support from the National Chicken Council, National Turkey Federation, United Egg Producers.
Contact Us
Thank you for your interest! We are pleased to receive inquiries from potential collaborators, journalists, and those with questions about our research.